Точка пересечения чевиан \(\displaystyle AP\) и \(\displaystyle CQ\) лежит на биссектрисе угла \(\displaystyle B\) треугольника \(\displaystyle ABC\small.\) Найдите \(\displaystyle PC\small,\) если \(\displaystyle AQ=4,\,BQ=6,\,BP=5\small.\)
| Обозначим длину отрезка \(\displaystyle PC\) за \(\displaystyle x\small.\) | 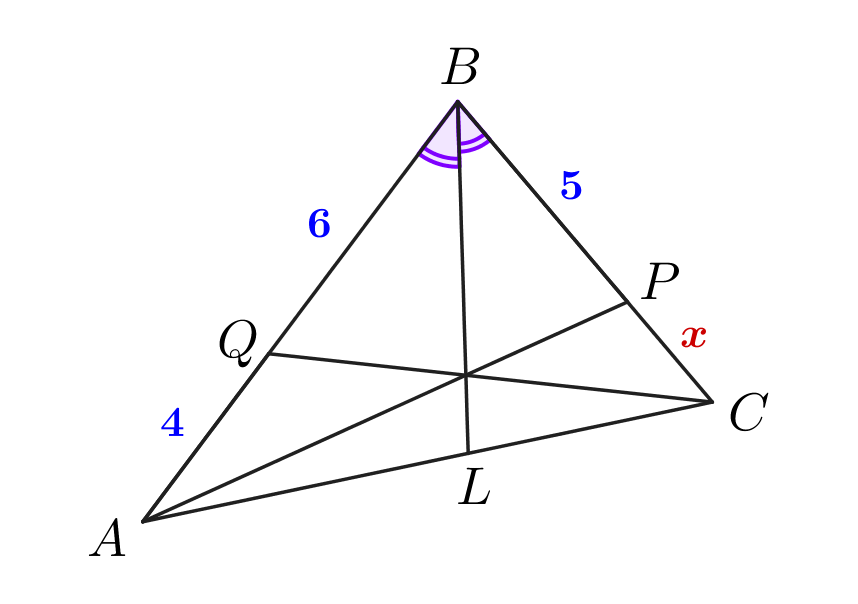 |
Отрезки \(\displaystyle AP,\,BL\) и \(\displaystyle CQ\) пересекаются в одной точке. Тогда по тереме Чевы: \(\displaystyle \frac{\color{blue}{AQ}}{\color{red}{QB}}\cdot\frac{\color{blue}{BP}}{\color{red}{PC}}\cdot\frac{\color{blue}{CL}}{\color{red}{LA}}=1\small.\) Подставим известные значения \(\displaystyle AQ=4,\,BQ=6,\,BP=5,\,CP=x{\small:}\) \(\displaystyle 1=\frac{4}{6}\cdot\frac{5}{x}\cdot\frac{CL}{AL}\small.\) | 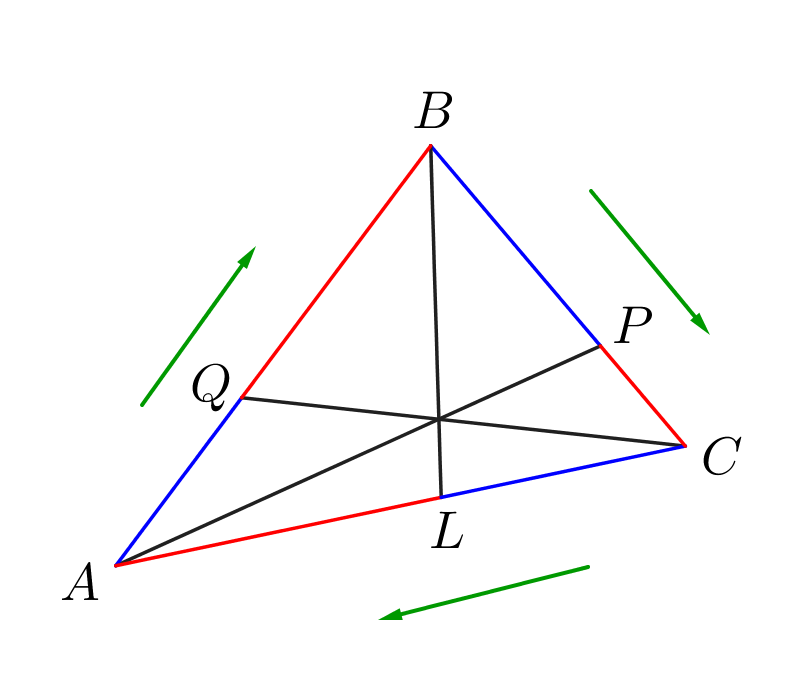 |
Также, поскольку \(\displaystyle \color{orange}{BL}\) – биссектриса, то по свойству биссектрисы: \(\displaystyle \frac{\color{blue}{CL}}{\color{green}{AL}}=\frac{\color{blue}{CB}}{\color{green}{AB}}=\frac{5+x}{4+6}=\frac{x+5}{10}\small.\) Получаем: \(\displaystyle 1=\frac{4}{6}\cdot\frac{5}{x}\cdot\frac{x+5}{10}\small.\) | 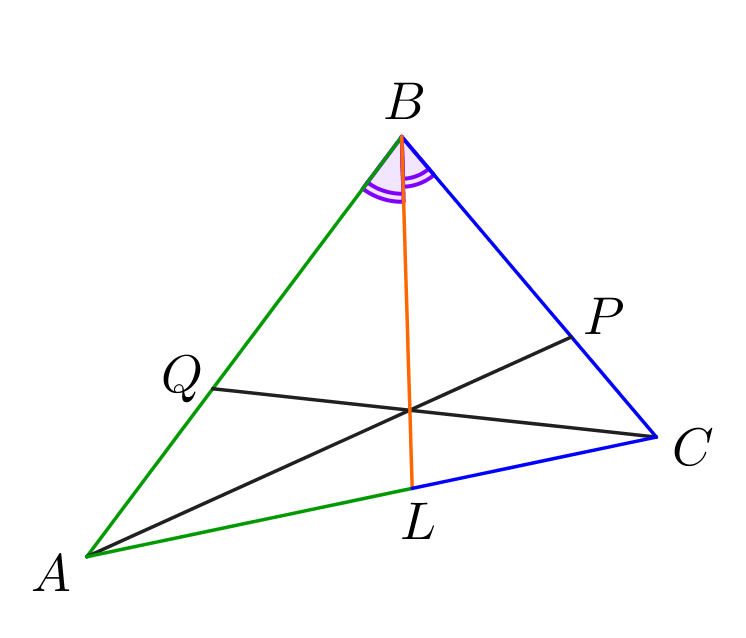 |
\(\displaystyle x=2{,}5\)
То есть \(\displaystyle CP=x=2{,}5\small.\)
Ответ: \(\displaystyle PC=2{,}5\small.\)